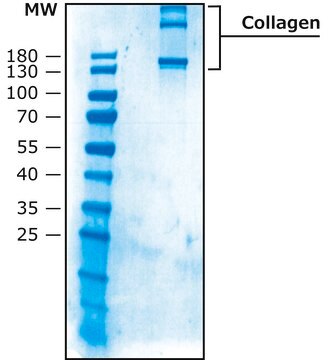
H4417
Human Collagen Type IV
from human placenta, liquid, High Performance
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
product name
Kollagen aus menschlicher Placenta, Bornstein and Traub Type IV, solution, suitable for cell culture, High Performance
Biologische Quelle
human placenta
Qualitätsniveau
Form
solution
Methode(n)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
Oberflächendeckung
<5 μg/cm2
Verunreinigungen
Endotoxin, tested
HIV, hepatitis B and hepatitis C, none detected
Lagertemp.
−20°C
Angaben zum Gen
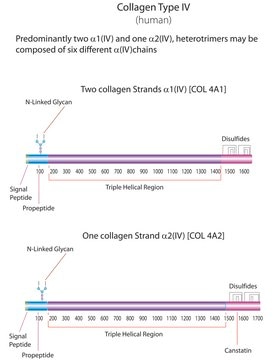
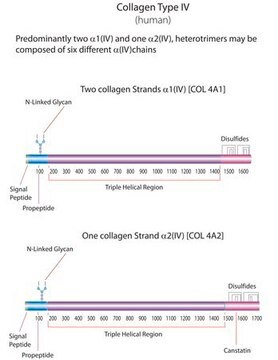
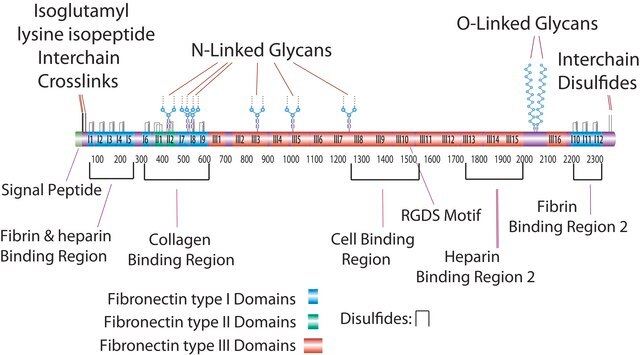
human ... COL4A1(1282) , COL4A2(1284) , COL4A3(1285) , COL4A4(1286) , COL4A5(1287) , COL4A6(1288)
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Anwendung
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Tissue injury in the autoimmune disease Goodpasture syndrome is due to pathogenic autoantibodies targeting the Collagen IV α3 chain . Mutations in COL4A5 are associated with Alport syndrome.
Komponenten
Vorsicht
Angaben zur Herstellung
Sonstige Hinweise
WGK
WGK 1
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.