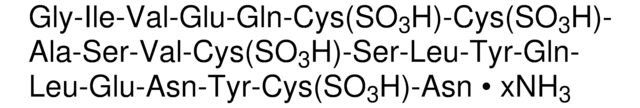R5250
Ribonuclease A from bovine pancreas
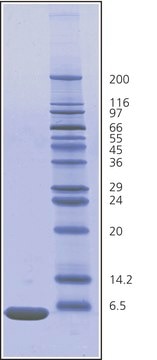
Type X-A, ≥90% (SDS-PAGE), ≥70 Kunitz units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
Pancreatic Ribonuclease, RNAsea, RNase A, Ribonucleate 3′-pyrimidinooligonucleotidohydrolase
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
bovine pancreas
Quality Level
type
Type X-A
assay
≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
form
buffered aqueous solution
specific activity
≥70 Kunitz units/mg protein
mol wt
~13,700
foreign activity
protease, essentially free
storage temp.
−20°C
InChI
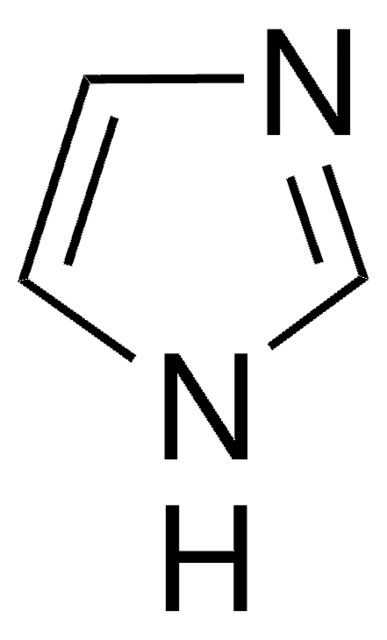
1S/C9H14N4O3/c10-2-1-8(14)13-7(9(15)16)3-6-4-11-5-12-6/h4-5,7H,1-3,10H2,(H,11,12)(H,13,14)(H,15,16)
InChI key
CQOVPNPJLQNMDC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
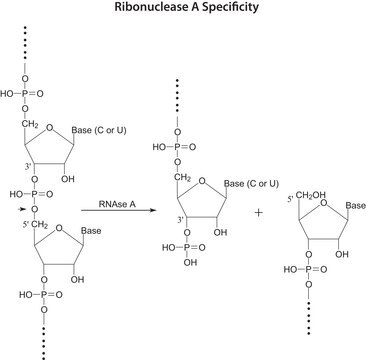
General description
Application
- RNase A is used to remove RNA from DNA plasmid and genomic DNA preparations and protein samples.
- RNase A is also used in RNA sequence analysis and protection assays.
- RNase A has been used as a tool for computer-aided drug design.
- RNase A supports the analysis of RNA sequences.
- RNase A hydrolyze RNA contained in protein samples.
- Purification of DNA is supported by RNase A.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
Physical form
Preparation Note
Analysis Note
inhibitor
signalword
Danger
hcodes
pcodes
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
wgk_germany
WGK 2
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service