U-2 OS Cell Line human
92022711, human bone, Not specified
Synonym(s):
U-2OS Cells, U2-OS Cells, U20S Cells, U2OS Cells
About This Item
Recommended Products
product name
U-2 OS Cell Line human, osteosarcoma, 92022711
biological source
human bone
growth mode
Adherent
karyotype
Not specified
morphology
Not specified
products
Not specified
receptors
Not specified
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
relevant disease(s)
cancer
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−196°C
Related Categories
Cell Line Origin
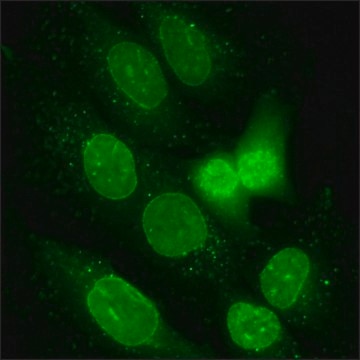
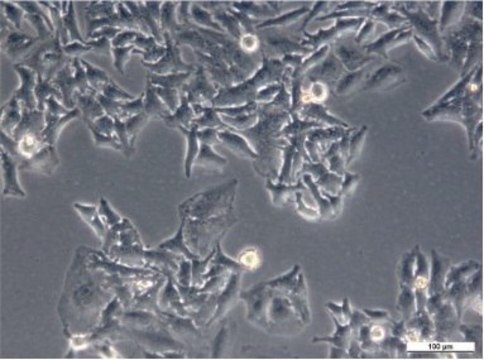
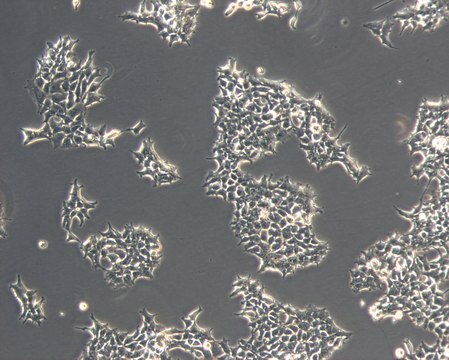
Cell Line Description
Application
- the importance of cyclin D1 for the activity of lithocholic acid hydroxyamide (LCAHA)
- the interaction of human single-stranded DNA binding protein 1 (hSSB1) with bloom syndrome protein helicase (BLM helicase)
- calcium-mediated actin reset (CaAR) in response to physiological changes
DNA Profile
CSF1PO: 13
D13S317: 13
D16S539: 11,12
D5S818: 11
D7S820: 11,12
THO1: 6,9.3
TPOX: 11,12
vWA: 14,18
Culture Medium
Subculture Routine
Other Notes
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
Regulation of the cell cycle involves processes crucial to the survival of a cell, including the detection and repair of genetic damage as well as the prevention of uncontrolled cell division associated with cancer. The cell cycle is a four-stage process in which the cell 1) increases in size (G1-stage), 2) copies its DNA (synthesis, S-stage), 3) prepares to divide (G2-stage), and 4) divides (mitosis, M-stage). Due to their anionic nature, nucleoside triphosphates (NTPs), the building blocks of both RNA and DNA, do not permeate cell membranes.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service