900628
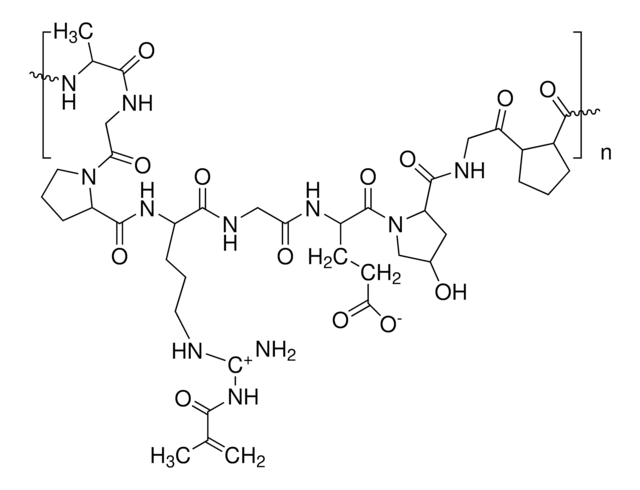
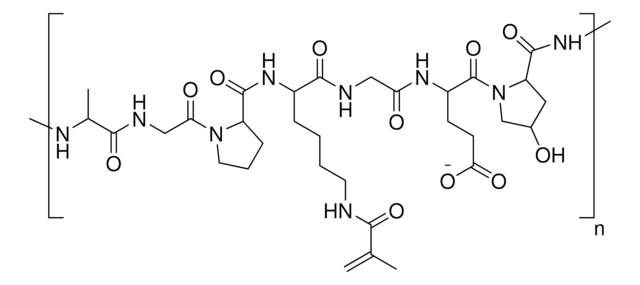
Gelatine-Methacryloyl
gel strength 90-110 g Bloom, degree of substitution 60%
Synonym(e):
GelMa, Gelatine-Methacrylamid, Gelatine-Methacrylat
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Verwandte Kategorien
Anwendung
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
Discussion of synthetic modifications to gelatin, improving the three-dimensional (3D) print resolution, and resulting material properties.
Professor Shrike Zhang (Harvard Medical School, USA) discusses advances in 3D-bioprinted tissue models for in vitro drug testing, reviews bioink selections, and provides application examples of 3D bioprinting in tissue model biofabrication.
Professor Shrike Zhang (Harvard Medical School, USA) discusses advances in 3D-bioprinted tissue models for in vitro drug testing, reviews bioink selections, and provides application examples of 3D bioprinting in tissue model biofabrication.
Protokolle
Frequently asked questions (FAQs) for KAPA SYBR® FAST One-Step qRT-PCR Kits.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.