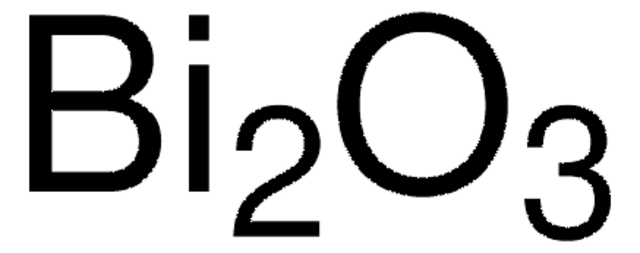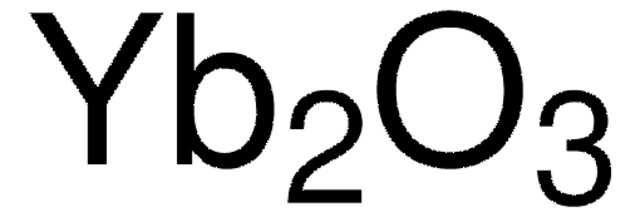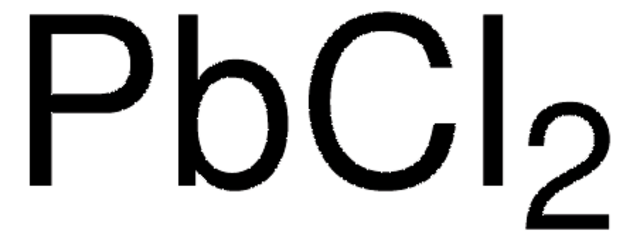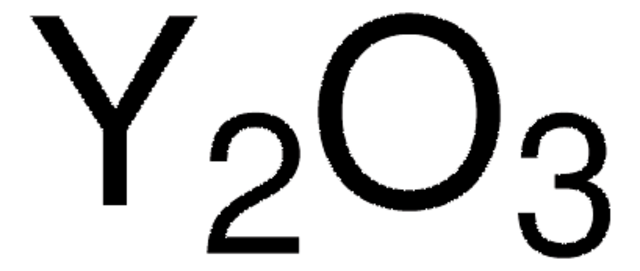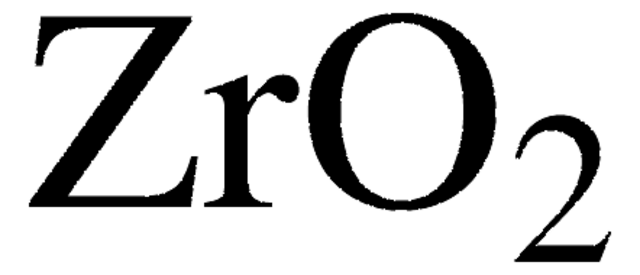637017
Bismut(III)-Oxid
nanopowder, 90-210 nm particle size, 99.8% trace metals basis
Synonym(e):
Dibismuttrioxid
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Beschreibung
beta
Qualitätsniveau
Assay
99.8% trace metals basis
Form
nanopowder
spherical
Eignung der Reaktion
reagent type: catalyst
core: bismuth
Oberflächenbereich
3.2-3.5 m2/g
Partikelgröße
90-210 nm
Schüttdichte
0.5‑1.1 g/mL
SMILES String
O=[Bi]O[Bi]=O
InChI
1S/2Bi.3O
InChIKey
WMWLMWRWZQELOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Anwendung
- Characterization and Physical Properties of Nano-sized Bi2O3/Polymer: This research investigates the properties of bismuth(III) oxide nanoparticles within a polymer matrix, emphasizing energy and high-refractive index applications. It explores the potential of Bi2O3 in enhancing the performance of composite materials (A Alruwaili, AM El Sayed, 2024).
- Electroanalytical Performance Enhancement by Bismuth (III) Oxide: A study on incorporating bismuth(III) oxide nanoparticles into carbon ceramic electrodes to improve their electroanalytical capabilities, particularly for detecting pollutants in water (M Brycht et al., 2024).
- Visible Light Responsive Photocatalysts for Arsenic Remediation: This review highlights the role of bismuth-based photocatalysts, including bismuth(III) oxide, in the effective remediation of arsenic from water sources, underlining the photocatalytic capabilities of these materials (I Natali Sora et al., 2024).
- High-Performance Composites for Gamma-Ray Shielding: An investigation into fluoroelastomer composites filled with bismuth(III) oxide for their application in gamma-ray shielding, highlighting the material′s effectiveness in blocking radiation (SM Magnere et al., 2024).
Leistungsmerkmale und Vorteile
WGK
nwg
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
Innovation in dental restorative materials is driven by the need for biocompatible and natural-appearing restoration alternatives. Conventional dental materials like amalgam and composite resins have inherent disadvantages.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.