D6883
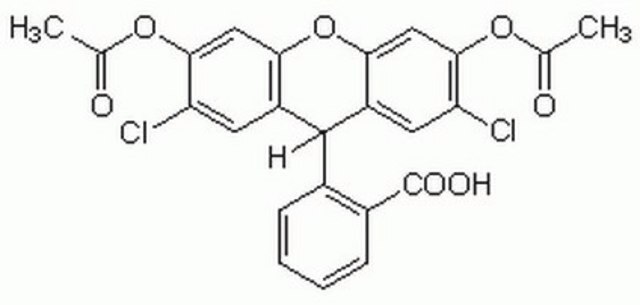
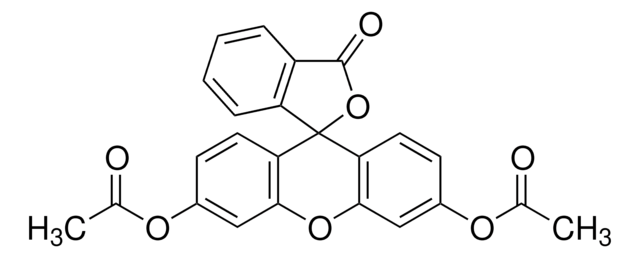
2′,7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate
≥97%
Synonym(s):
2′,7′-Dichlorofluorescin diacetate, 2′,7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
assay
≥97%
form
powder
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
CC(=O)Oc1cc2Oc3cc(OC(C)=O)c(Cl)cc3C(c2cc1Cl)c4ccccc4C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C24H16Cl2O7/c1-11(27)31-21-9-19-15(7-17(21)25)23(13-5-3-4-6-14(13)24(29)30)16-8-18(26)22(32-12(2)28)10-20(16)33-19/h3-10,23H,1-2H3,(H,29,30)
InChI key
PXEZTIWVRVSYOK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
Application
- sensitive and rapid quantitation of oxygen-reactive species in response to oxidative metabolism
- microplate assay for detecting oxidative products in phagocytic cells
- quantitative multiwell myeloid differentiation assay
Storage and Stability
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Oxidative stress is mediated, in part, by reactive oxygen species produced by multiple cellular processes and controlled by cellular antioxidant mechanisms such as enzymatic scavengers or antioxidant modulators. Free radicals, such as reactive oxygen species, cause cellular damage via cellular.
Related Content
DISCOVER Bioactive Small Molecules for Nitric Oxide & Cell Stress Research
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service