B20223
Collagenase - DNase I - Dispase II blend
Tissue dissociation blend, lyophilized powder, suitable for cell culture
Synonym(s):
Clostridiopeptidase A, Clostridium histolyticum, DNase I, Deoxyribonuclease I, Deoxyribonucleate 5′-oligonucleotido-hydrolase, Dispase II, Protease from Bacillus polymyxa, collagenase, collagenase blend, enzyme blend, tissue dissociation blend
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
≥2 units/mL Dispase II
concentration
0.1 mg/mL (DNase)
1 mg/mL (collagenase)
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
-10 to -25°C
Related Categories
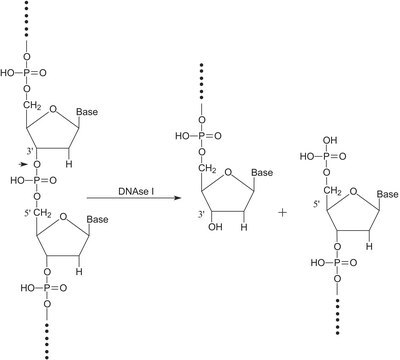
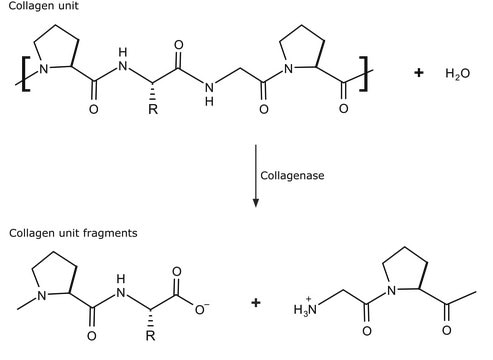
General description
Biochem/physiol Actions
Preparation Note
signalword
Danger
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service