A9934
Aminopeptidase I from Streptomyces griseus
lyophilized powder, ≥200 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
Leucine Aminopeptidase IV
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
General description
Aminopeptidase I from Streptomyces griseus is a thermostable enzyme with Glu131 and Tyr246 as key active site residues.
Application
Aminopeptidase I from Streptomyces griseus has been used:
- to test the biochar exposure effect on the enzyme activity
- in circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy studies
- as a positive control in p-nitroanilide degradation assay
Biochem/physiol Actions
Aminopeptidase I from S. griseus has a fairly broad specificity, being able to remove the N-terminal residue of most proteins, except where the penultimate residue is an imino acid. It contains two Zn2+ binding sites. Aminopeptidase I from S. griseus is inhibited by 1,10-phenanthroline and is activated six-fold by Ca2+, which also stabilizes it against heat inactivation. This monomeric zinc metalloprotein has an isoelectric point (pI) of 5.4.
Aminopeptidase I may also be used as a reagent in the assay of endoprotease activities with a synthetic substrate in a two-stage assay. In the first stage, the endoprotease cleaves a peptide, such as Z-Y-X-Leu-p-nitroanilide, with the X, Y, and Z residues being chosen according to the specificity of the endoprotease.
Packaging
Package size based on protein content.
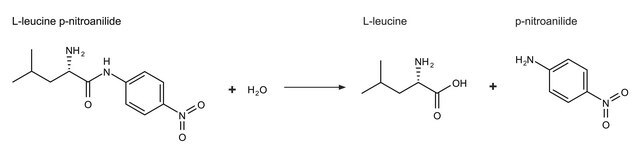
Unit Definition
One unit will hydrolyze 1.0 μmole of L-leucine-p-nitroanilide to L-leucine and p-nitroaniline per min at pH 8.0, 25 °C and 3.0 mM substrate concentration.
Physical form
Contains calcium acetate
Preparation Note
Reconstitute in 20 mM tricine, pH 8.0, with 0.05% bovine serum albumin. Dilute the enzyme with the reconstitution buffer to 0.15-0.3 U/mL for a working concentration. Solutions should be prepared fresh prior to use.
Other Notes
Endopeptidase contaminant: Not more than: 0.01 U/mg protein (as μmole tyrosine equivalent per min released from casein.)
signalword
Danger
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
[Autophagy related genes in yeast, S. cerevisiae].
Yoshinori Ohsumi
Tanpakushitsu kakusan koso. Protein, nucleic acid, enzyme, 51(10 Suppl), 1453-1456 (2006-08-23)
Indig, F.E., et al.
Febs Letters, 225, 237-237 (1989)
Taras Y Nazarko et al.
Autophagy, 1(1), 37-45 (2006-07-29)
Yarrowia lipolytica was recently introduced as a new model organism to study peroxisome degradation in yeasts. Transfer of Y. lipolytica cells from oleate/ethylamine to glucose/ammonium chloride medium leads to selective macroautophagy of peroxisomes. To decipher the molecular mechanisms of macropexophagy
A Spungin et al.
European journal of biochemistry, 183(2), 471-477 (1989-08-01)
A heat-stable aminopeptidase with an N-terminal Ala-Pro-Asp-Ile-Pro-Leu sequence has been purified from Streptomyces griseus by heat treatment followed by gel-exclusion and anion-exchange chromatographic procedures. The enzyme is a monomeric zinc metalloenzyme showing an apparent molecular mass of 33 kDa by
Congcong He et al.
Molecular biology of the cell, 19(12), 5506-5516 (2008-10-03)
Autophagy is the degradation of a cell's own components within lysosomes (or the analogous yeast vacuole), and its malfunction contributes to a variety of human diseases. Atg9 is the sole integral membrane protein required in formation of the initial sequestering
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service