2106
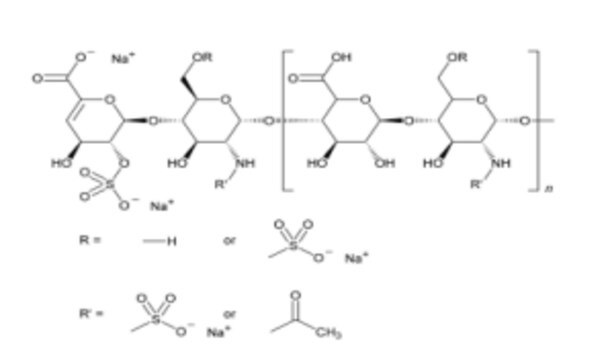
Heparin sodium salt from porcine intestinal mucosa
endotoxin, free
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
Porcine intestinal mucosa
Quality Level
form
powder
usage
sufficient for 5 mL blood anticoagulant
packaging
preweighed vial of 300 USP units
impurities
endotoxin, free
color
beige
solubility
water: soluble 50 g/L
acetone: insoluble
alcohol: insoluble
benzene: insoluble
chloroform: insoluble
diethyl ether: insoluble
compatibility
for use with E-Toxate™
storage temp.
room temp
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Caution
Other Notes
Legal Information
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 2
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service