SCC623
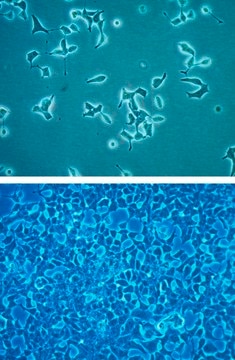
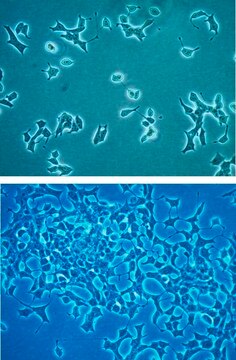
MIN6 Mouse Insulinoma Cell Line

Synonym(s):
MIN-6, Min6, Min6 cells, Mouse INsulinoma 6
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
41106514
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
packaging
vial of ≥1 x 10^6 vial (viable cells per vial)
manufacturer/tradename
Millipore
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
shipped in
liquid nitrogen
storage temp.
−196°C
Application
- Cells are verified to be of mouse origin and negative for human, rat, Chinese hamster, Golden Syrian hamster, and non-human primate interspecies contamination, as assessed by a Contamination Clear panel by Charles River Animal Diagnostic Services
- Cells tested negative for infectious diseases against a Mouse Essential CLEAR panel by Charles River Animal Diagnostic Services.
- Cells tested negative for mycoplasma.
Features and Benefits
The MIN6 cell line is a long-term stable mouse pancreatic beta-cell line that retains characteristics of mature β-cells and can be used to analyze insulin secretion/sensitivity in diabetes research.
Target description
The Mouse Insulinoma Cell Line (MIN6), was derived from an insulinoma tissue that developed in a transgenic mouse in which the expression of the Simian Virus 40 Large T antigen was driven by the human insulin promoter.1,2,3 In comparison to the primary pancreatic b-cells, MIN6 thrives reliably and far more robustly in cell culture and yet retains the important characteristics of the b-cells, such as the exclusive expression of the so-called “liver-type” glucose transporter (Glut2) and their ability to modulate the insulin secretion in response to the changing glucose concentration in the growth medium, and it has been a staple strain in diabetes research since its establishment in 1990.
Additionally, the expression of the major histocompatibility complex I (MHC I) is lacking in MIN6, as in the non-diabetic b-cells, but can be induced by pro-inflammatory cytokines,1,4,5 which would render them susceptible to T-cell mediated cytotoxicity. This closely mimics the behavior of the b-cells isolated from diabetic tissues, where chronic inflammation is commonly observed, and it has made MIN6 an attractive cell line model for investigating the mechanism of the b-cells loss due to their autoimmune destruction.
References
1. Miyazaki J, Araki K, Yamato E, Ikegami H, Asano T, Shibasaki Y, Oka Y, Yamamura K. 1990. Establishment of a pancreatic beta cell line that retains glucose-inducible insulin secretion: special reference to expression of glucose transporter isoforms. Endocrinology. 27(1):126-32.
2. Sarvetnick N, Liggitt D, Pitts SL, Hansen SE, Stewart TA. 1988. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus induced in transgenic mice by ectopic expression of class II MHC and interferon-gamma. Cell. 52(5):773-82. Pytynia KB, Dahlstrom KR, Sturgis EM. 2014. Epidemiology of HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 50(5): 380-6.
3. Ullrich A, Dull TJ, Gray A, Philips JA 3rd, Peter S. 1982. Variation in the sequence and modification state of the human insulin gene flanking regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 10(7):2225-40.
4. Jiang H, Li Y, Shen M, Liang Y, Qian Y, Dai H, Xu K, Xu X, Lv H, Zhang J, Yang T, Fu Q. 2022. Interferon-α promotes MHC I antigen presentation of islet α cells through STAT1-IRF7 pathway in type 1 diabetes. Immunology. 166(2):210-221.
5. Javeed N, Her TK, Brown MR, Vanderboom P, Rakshit K, Egan AM, Vella A, Lanza I, Matveyenko AV. 2021. Pro-inflammatory α cell small extracellular vesicles induce α cell failure through activation of the CXCL10/CXCR3 axis in diabetes. Cell Rep. 36(8):109613.
Additionally, the expression of the major histocompatibility complex I (MHC I) is lacking in MIN6, as in the non-diabetic b-cells, but can be induced by pro-inflammatory cytokines,1,4,5 which would render them susceptible to T-cell mediated cytotoxicity. This closely mimics the behavior of the b-cells isolated from diabetic tissues, where chronic inflammation is commonly observed, and it has made MIN6 an attractive cell line model for investigating the mechanism of the b-cells loss due to their autoimmune destruction.
References
1. Miyazaki J, Araki K, Yamato E, Ikegami H, Asano T, Shibasaki Y, Oka Y, Yamamura K. 1990. Establishment of a pancreatic beta cell line that retains glucose-inducible insulin secretion: special reference to expression of glucose transporter isoforms. Endocrinology. 27(1):126-32.
2. Sarvetnick N, Liggitt D, Pitts SL, Hansen SE, Stewart TA. 1988. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus induced in transgenic mice by ectopic expression of class II MHC and interferon-gamma. Cell. 52(5):773-82. Pytynia KB, Dahlstrom KR, Sturgis EM. 2014. Epidemiology of HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 50(5): 380-6.
3. Ullrich A, Dull TJ, Gray A, Philips JA 3rd, Peter S. 1982. Variation in the sequence and modification state of the human insulin gene flanking regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 10(7):2225-40.
4. Jiang H, Li Y, Shen M, Liang Y, Qian Y, Dai H, Xu K, Xu X, Lv H, Zhang J, Yang T, Fu Q. 2022. Interferon-α promotes MHC I antigen presentation of islet α cells through STAT1-IRF7 pathway in type 1 diabetes. Immunology. 166(2):210-221.
5. Javeed N, Her TK, Brown MR, Vanderboom P, Rakshit K, Egan AM, Vella A, Lanza I, Matveyenko AV. 2021. Pro-inflammatory α cell small extracellular vesicles induce α cell failure through activation of the CXCL10/CXCR3 axis in diabetes. Cell Rep. 36(8):109613.
Storage and Stability
The cells should be stored in liquid nitrogen. The cells can be cultured for at least 10 passages after initial thawing without significantly affecting the cell marker expression and functionality.
Other Notes
This product is intended for sale and sold solely to academic institutions for internal academic research use per the terms of the “Academic Use Agreement” as detailed in the product documentation. For information regarding any other use, please contact licensing@emdmillipore.com.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service