SCC205
LUVA Human Mast Cell Line

Synonym(s):
Laboratory of University of VirginiA Cell Line
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
41106514
Recommended Products
biological source
human
Quality Level
packaging
vial of ≥1X10⁶ cells/vial vial
manufacturer/tradename
Millipore
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
shipped in
liquid nitrogen
storage temp.
−196°C
Application
- Each vial contains >1X106 viable cells.
- Cells are tested negative for infectious diseases by a Mouse Essential CLEAR Panel by Charles River Animal Diagnostic Services.
- Cells are verified to be of human origin and negative for interspecies contamination from human, rat, Chinese hamster, Golden Syrian hamster, and nonhuman primate (NHP) as assessed by a Contamination Clear panel by Charles River Animal Diagnostic Services
- Cells are negative for mycoplasma contamination.
Features and Benefits
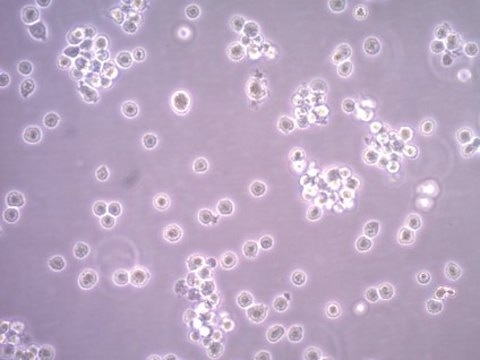
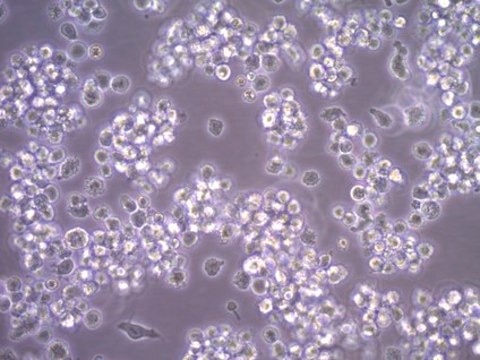
The LUVA cell line is a human mast cell in vitro cell model used to study the mechanisms which cause mastocytosis, inflamation and allergic responses.
Target description
Mast cells are a type of granulocyte that are important components for the immune system and the process of inflammation. When activated, they will release compounds inducing an inflammatory response and anaphylaxis. They are also directly involved in causing allergies and related disorders. Previously, mast cell lines such as LAD2 were used as in vitro cell models for studying mast cells. However, they were unstable and inconsistent for culturing.1A new mast cell line was developed and given the name of LUVA cells, which mirror the morphology and functionality of human mast cells.
The CD34+ mast cells were cultured for 8 weeks with stem cell factor and cultured with IL-6 and IL-3 for only one week. The stable LUVA cells were maintained and became capable of growing without further addition of growth factors in culture, making them highly convenient for culturing. They are the first mast cell line in which the donor patient did not have a mast cell disorder, as well as having no mutation in the c-kit receptor.1
The LUVA cell line allows for a proper in vitro mast cell model in which researchers can study the mechanisms which cause mastocytosis, a condition where mast cells aggregate in certain parts of the body.2 This condition results in a higher risk of life-threatening allergic reactions as well as rarely resulting in mast cell cancers. Commonly, mastocytosis is caused by a mutation of the c-KIT protein, a receptor tyrosine kinase. By understanding c-KIT mechanisms, therapies can continue to develop and improve for mastocytosis patients.
Source: The LUVA mast cell line was derived from CD34+ cells of a non-mastocytosis donor with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease.
References
1. Laidlaw, T.M., et al. Characterization of a novel human mast cell line that responds to stem cell factor and expresses functional FcεRI. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 127:815-822.e5 (2011)
The CD34+ mast cells were cultured for 8 weeks with stem cell factor and cultured with IL-6 and IL-3 for only one week. The stable LUVA cells were maintained and became capable of growing without further addition of growth factors in culture, making them highly convenient for culturing. They are the first mast cell line in which the donor patient did not have a mast cell disorder, as well as having no mutation in the c-kit receptor.1
The LUVA cell line allows for a proper in vitro mast cell model in which researchers can study the mechanisms which cause mastocytosis, a condition where mast cells aggregate in certain parts of the body.2 This condition results in a higher risk of life-threatening allergic reactions as well as rarely resulting in mast cell cancers. Commonly, mastocytosis is caused by a mutation of the c-KIT protein, a receptor tyrosine kinase. By understanding c-KIT mechanisms, therapies can continue to develop and improve for mastocytosis patients.
Source: The LUVA mast cell line was derived from CD34+ cells of a non-mastocytosis donor with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease.
References
1. Laidlaw, T.M., et al. Characterization of a novel human mast cell line that responds to stem cell factor and expresses functional FcεRI. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 127:815-822.e5 (2011)
Storage and Stability
LUVA human mast cells should be stored in liquid nitrogen. The cells can be cultured for at least 10 passages without significantly affecting cell marker expression and function.
Other Notes
This product is intended for sale and sold solely to academic institutions for internal academic research use per the terms of the “Academic Use Agreement” as detailed in the product documentation. For information regarding any other use, please contact licensing@emdmillipore.com.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service