180947
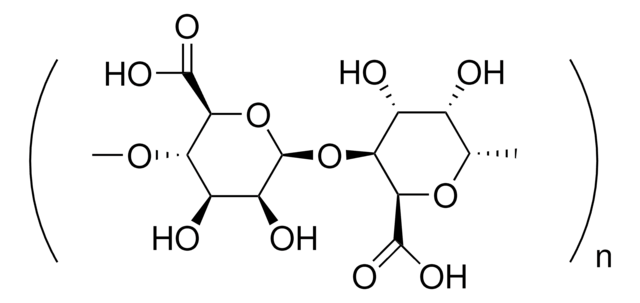
Alginic acid sodium salt
powder
Synonym(s):
Algin, Sodium alginate
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
algae (marine)
Quality Level
form
powder
viscosity
15-25 cP, 1 % in H2O
InChI
1S/C6H10O7.Na/c7-1-2(8)4(5(10)11)13-6(12)3(1)9;/h1-4,6-9,12H,(H,10,11);/q;+1/p-1/t1-,2-,3-,4?,6+;/m0./s1
InChI key
MSXHSNHNTORCAW-MPGIDXPLSA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
- in combination with chitosan, to fabricate a biodegradable porous scaffold for bone tissue engineering.
- to study the characteristics of a modified amphiphilic alginate derivative
- to the study the impact of alginate on the rate of lipid digestion by employing an in vitro digestion model
- in the preparation of alginate hydrogels
- as encapsulating agents of microparticles of β-galactosidae
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
Chitosan is a naturally occurring polysaccharide ideally suited for use in medical supplies, devices, therapeutics, and diagnostics. The unique natural characteristics of chitosan include its cationic, biocompatible, biodegradable, non-toxic, non-immunogenic, and antimicrobial properties.
Collagen molecules play a critical role in tissue architecture and strength, and in cell-matrix interactions as insoluble ligands to regulate the diverse phenotypic activities of cells.
The use of hydrogel-based biomaterials for the delivery and recruitment of cells to promote tissue regeneration in the body is of growing interest. This article discussed the application of hydrogels in cell delivery and tissue regeneration.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service