General description
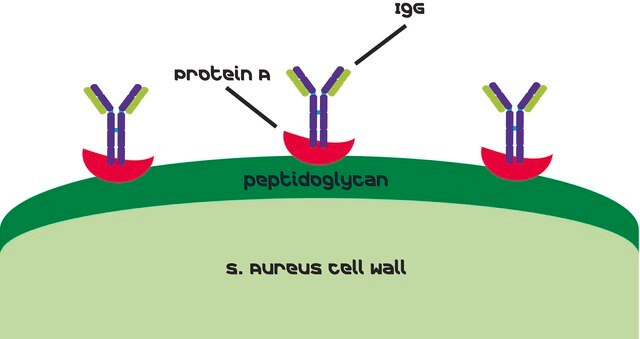
Protein A is a 42 kD, highly stable cell surface receptor isolated from Staphylococcus aureus which binds selectively and with high affinity to the Fc portion of IgG from various species. It can also be immobilized on solid support like agarose or acrylic beads and is used for purification of monoclonal or polyclonal immunoglobulins. Protein A reacts specifically to IgG of monkey, rabbit, pig, guinea pig, dog, and cat.
Application
Protein A may be used for immunoprecipitation assays . It can be conjugated to fluorescent dyes, enzyme markers, biotin or colloidal gold and can be used in immunohistochemistry, western blotting and ELISA.
Suspension may be used directly as an immunoadsorbent. Not intended for use as a starter culture.
Protein A may be conjugated with various reporter molecules including fluorescent dyes (FITC), enzyme markers (peroxidase, β-galactosidase, alkaline phosphatase), biotin, and colloidal gold without affecting the antibody binding site on the molecule. These conjugates are used to detect immunoglobulins in various immunochemical assays including western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA applications. In addition, protein A may be immobilized on a solid support such as agarose or acrylic beads for the purification of either polyclonal or monoclonal immunoglobulins. It is also routinely used for immunoprecipitation assays.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Protein A is a highly stable cell surface receptor produced by several strains of Staphylococcus aureus. It consists of a single polypeptide chain of molecular weight 42 kDa, containing four repetitive domains rich in aspartic and glutamic acids but devoid of cysteine. It contains little or no carbohydrate and only 4 tyrosine residues and no tryptophans. Protein A is capable of binding to the Fc portion of immunoglobulins, especially IgGs, from a large number of species. One protein A molecule has been shown to bind at least 2 molecules of IgG simultaneously. The IgG binding domain of Protein A consists of three anti-parallel α-helicies, the third of which is disrupted when the protein is complexed with the Fc region of the immunoglobulins. Protein A will bind the Fc portion of human IgG subclasses, IgM, IgA and IgE; and mouse IgG1 (weakly), IgG2a, and IgG2b. Protein A also binds IgGs from other species, including monkey, rabbit, pig, guinea pig, dog, and cat.
Protein A also participates in a number of different protective biological functions including anti-tumor, toxic, and carcinogenic activities. In addition to acting as an immunomodulator, it also has antifungal and antiparasitic properties.
Physical form
~10% (wet weight/volume) of essentially non-viable S. aureus (Cowan strain) cells in 0.04 M potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.2, 0.15 M sodium chloride containing 0.2% sodium azide.
Preparation Note
Prepared by a method developed in our laboratory to ensure reproducible binding of IgG.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.