G8404
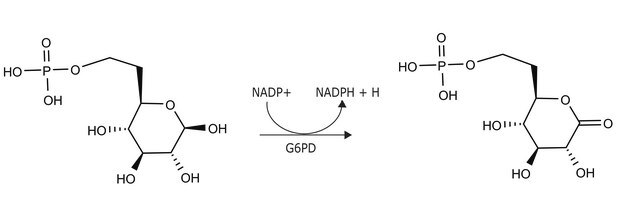
Glucose-6-phosphate Dehydrogenase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, ammonium sulfate suspension, ≥550 units/mg protein (biuret)
Synonym(s):
Entner-Doudoroff enzyme, G6PD, G6PDH, NADP glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase, G-6-P-DH
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
bacterial (Leuconostoc mesenteroides)
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
form
ammonium sulfate suspension
specific activity
≥550 units/mg protein (biuret)
mol wt
128 kDa
storage condition
(Tightly closed)
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
UniProt accession no.
foreign activity
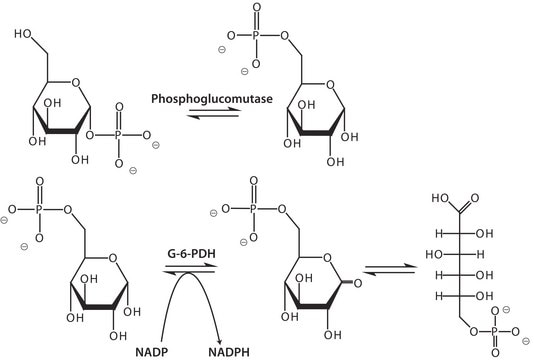
creatine phosphokinase, glutathione reductase, myokinase, NADH oxidase, NADPH oxidase, phosphoglucomutase, 6-phosphogluconic dehydrogenase, phosphoglucose isomerase, lactic dehydrogenase, hexokinase ≤0.01%
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Research area: Cell Signaling
Application
- to test ketose reductase activity in developing maize endosperm.
- to determine the levels of mannose in coronary heart disease patient-derived serum
- to study its activity on extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) extract to determine cell lysis through sonication
- to determine the glucose uptake in cultured human muscle satellite cells
Biochem/physiol Actions
Unit Definition
Physical form
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
EU REACH Annex XVII (Restriction List)
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Instructions for working with enzymes supplied as ammonium sulfate suspensions
Protocols
Enzymatic Assay of Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.49)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service