D8768
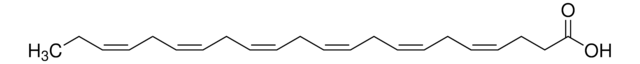
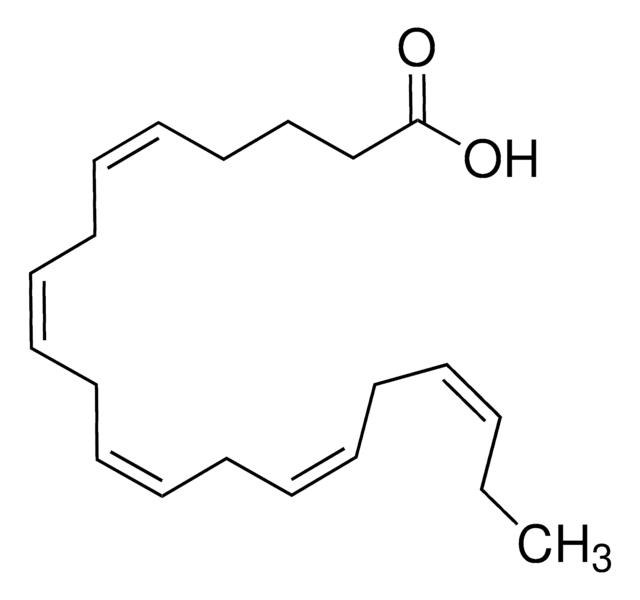
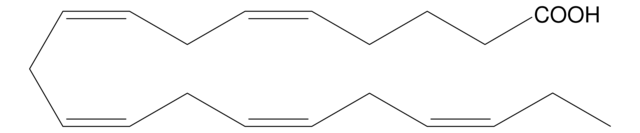
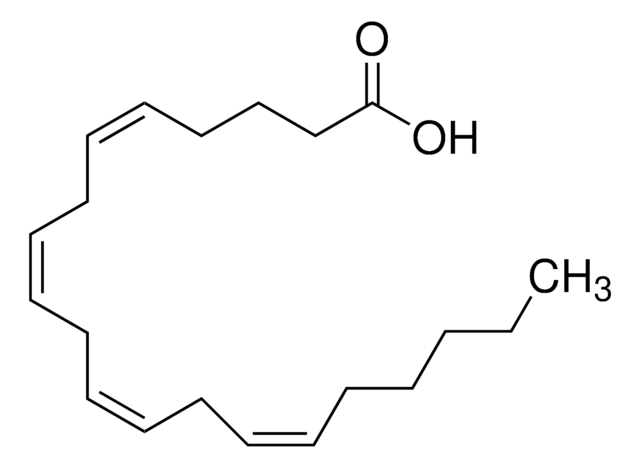
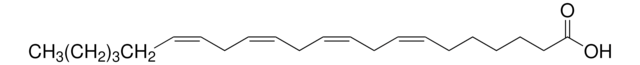
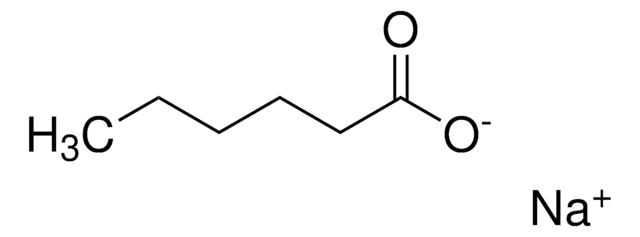
cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-Docosahexaenoic acid sodium salt
≥95%, waxy solid
Synonym(s):
Sodium (all-Z)-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoate
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
cod liver oil
Quality Level
Assay
≥95%
form
waxy solid
functional group
carboxylic acid
lipid type
omega FAs
shipped in
ambient
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
CC/C=C\C/C=C\C/C=C\C/C=C\C/C=C\C/C=C\CCC(O[Na])=O
InChI
1S/C22H32O2.Na/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18-19-20-21-22(23)24;/h3-4,6-7,9-10,12-13,15-16,18-19H,2,5,8,11,14,17,20-21H2,1H3,(H,23,24);/q;+1/p-1/b4-3-,7-6-,10-9-,13-12-,16-15-,19-18-;
InChI key
SNNDEWVSGZRIFE-FPYKSTABSA-M
Related Categories
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
The potential for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease through increased dietary intake of omega-3 (w-3) fish oils is not a recent scientific discovery.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service