A8582
Antifoam SE-15
aqueous emulsion for bacterial and mammalian systems
Synonym(s):
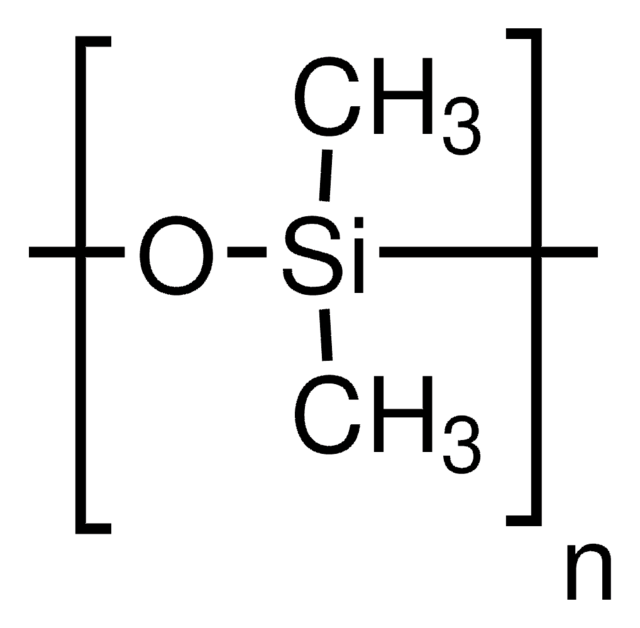
silicone-based antifoam
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12161901
NACRES:
NA.85
Recommended Products
Quality Level
form
emulsion (aqueous)
concentration
10% (active silicon)
technique(s)
cell culture | hybridoma: suitable
solubility
H2O: soluble (effective hot or cold.)
density
1.0 g/mL at 25 °C
application(s)
microbiology
storage temp.
room temp
suitability
(Mammalian (suspension))
bacteria (fermentation)
General description
Antifoam SE-15 is a silicone-based product used to prevent or minimize foaming in both microbial fermentation systems and mammalian suspension cultures. Control of foaming minimizes damage to the cells, resulting in increased protein/antibody production.
Application
Antifoam SE-15 has been used:
- in the preparation of ramified rolling circle amplification (RAM) amplification buffer.
- to find its effects on cell viability, virus infectivity and PCR (polymerase chain reaction) performance.
- as a constituent of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for the determination of total antioxidant status (TAOS) by 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) assay.
- as a component of autoinduction expression culture.
- as a component of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) detection buffer.
Features and Benefits
- Controls foaming in microbial culture flasks or fermentations
- Non-toxic to the culture medium
- Can be pumped to fermenter on an as-needed basis
Components
Antifoam SE-15 is an aqueous emulsion containing 10% active silicon and non-ionic emulsifiers .
Preparation Note
Antifoam SE-15 can be pre-diluted with 3-10 parts of cool water to aid in dispersion. Pre-diluted
suspensions should be used immediately.
suspensions should be used immediately.
related product
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - STOT RE 2 Inhalation
Target Organs
Lungs
WGK
WGK 1
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Dario A Vitturi et al.
American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology, 296(5), H1398-H1407 (2009-03-17)
Allosteric regulation of nitrite reduction by deoxyhemoglobin has been proposed to mediate nitric oxide (NO) formation during hypoxia. Nitrite is predominantly an anion at physiological pH, raising questions about the mechanism by which it enters the red blood cell (RBC)
Detection of nucleic acid targets using ramified rolling circle DNA amplification: a single nucleotide polymorphism assay model
Smith J H and Beals T P
PLoS ONE, 8(5), e65053-e65053 (2013)
Elisa Binda et al.
BMC biotechnology, 13, 24-24 (2013-03-19)
VanYn, encoded by the dbv7 gene (also known as vanYn) of the biosynthetic cluster devoted to A40926 production, is a novel protein involved in the mechanism of self-resistance in Nonomuraea sp. ATCC 39727. This filamentous actinomycete is an uncommon microorganism
James H Smith et al.
PloS one, 8(5), e65053-e65053 (2013-06-01)
Isothermal amplification methods provide alternatives to PCR that may be preferable for some nucleic acid target detection tasks. Among current isothermal target detection methods, ramified rolling circle amplification (RAM) of single-stranded DNA circles that are formed by ligation of linear
Jiayi Jin et al.
Insect biochemistry and molecular biology, 118, 103310-103310 (2019-12-25)
Many arthropod venom peptides have potential as bioinsecticides, drug leads, and pharmacological tools due to their specific neuromodulatory functions. Assassin flies (Asilidae) are a family of predaceous dipterans that produce a unique and complex peptide-rich venom for killing insect prey
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service