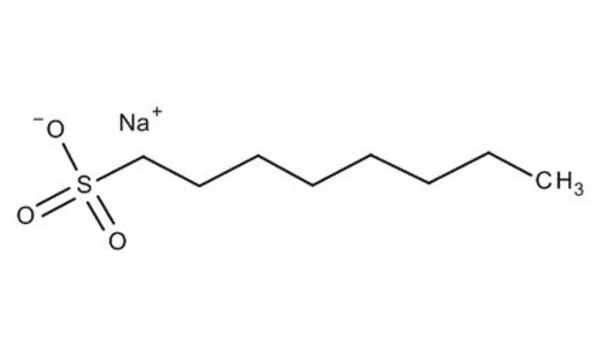
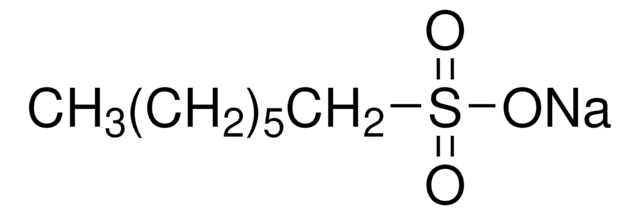H2766
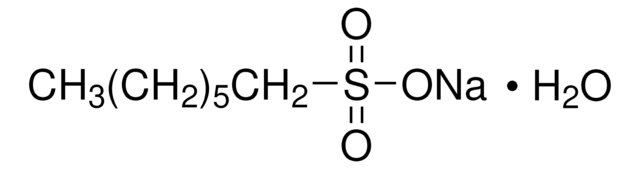
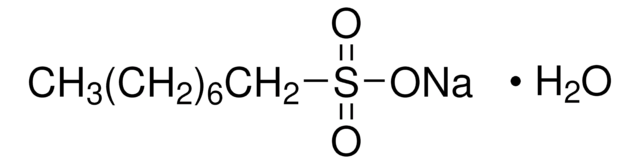
Sodium 1-heptanesulfonate
Synonym(s):
1-Heptanesulfonic acid sodium salt
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
synthetic (oragnic)
Quality Level
description
anionic
form
powder
mol wt
202.25 g/mol
technique(s)
HPLC: suitable
LC/MS: suitable
impurities
<2.0% water (Karl Fischer)
mp
300 °C (572 °F)
solubility
H2O: ≥100 mg/mL
cation traces
Na: 10.8-12.0 % (w/v) (anhydrous)
SMILES string
[Na+].CCCCCCCS([O-])(=O)=O
InChI
1S/C7H16O3S.Na/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-11(8,9)10;/h2-7H2,1H3,(H,8,9,10);/q;+1/p-1
InChI key
REFMEZARFCPESH-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
- Ideal for Cell Biology and Biochemical Research
- High purity chemical suitable for multiple research applications
Other Notes
comparable product
WGK
WGK 2
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
The liver excretes excess cholesterol in the form of bile acids. Bile acids serve two purposes: to remove unwanted cholesterol from the body and to aid in lipid digestion in the intestine.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service