Recommended Products
form
liquid
Quality Level
does not contain
preservative
manufacturer/tradename
Calbiochem®
storage condition
OK to freeze
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
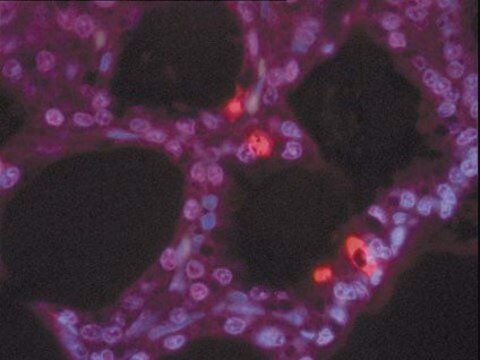
Native TdT from calf thymus. Tdt is a DNA polymerase that catalyzes the addition of deoxynucleotides to the 3′ hydroxy terminus of either double of single stranded DNA in a template-independent manner.
Native TdT from calf thymus. Tdt is a DNA polymerase that catalyzes the addition of deoxynucleotides to the 3′ hydroxy terminus of either double of single stranded DNA in a template-independent manner. Although TdT preferentially adds deoxynucleotides to 3′-extensions, tailing onto 5′ overhangs or blunt ended double strands of DNA can also be achieved. TdT can be used for labeling DNA fragments and vectors with homopolymer tails and/or with modified deoxynucleotides such as biotin-dNTPs, 32P-dNTPs, cordycepin-dNTPs, or ddNTP.
The Calbiochem® Terminal deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT) is a DNA polymerase isolated from calf thymus. TdT catalyzes the addition of deoxynucleotides to the 3′-hydroxyl termini of either double or single stranded DNA molecules in a template independent manner. Although TdT preferentially adds deoxynucleotides to 3′-extensions, tailing onto 5′ overhangs or blunt ended double strands of DNA can also be achieved. TdT can be used for labeling DNA fragments and vectors with homopolymer tails and/or with modified deoxynucleotides such as biotin-dNTPs, 32P-dNTPs, cordycepin-dNTPs, or ddNTP.
Application
DNA Labeling
Warning
Toxicity: Standard Handling (A)
Unit Definition
One unit is the amount of enzyme required to transfer 1 nmol of dAMP from dATP to the 3ʹ-OH terminus of d(A)50 in 60 min at 37°C.
Physical form
775 Units in 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer, 1 mM B-mercaptoethanol, 50% glycerol, pH 7.2.
Reconstitution
Following initial thaw, aliquot and freeze (-20°C).
Other Notes
Chang, L.M.S. and F.J. Bollum. 1986. Crit. Rev. Biochem.21, 27.
Deng, G. and R. Wu. 1983. Methods Enzymol. 100, 96.
Michelson, A.M. and S.H. Orkin. 1982. J. Biol. Chem.257, 14773.
Roychoudhury, R. and R. Wu. 1980. Methods Enzymol.65, 43.
Nelson, T. and D. Brutlag. 1979. Methods Enzymol. 68, 41.
Roychoudhury, R., et al. 1976. Nucleic Acids Res.3, 101.
Bollum, F.J. 1974. In The Enzymes, 3rd edition (ed. P.D. Boyer), Vol. 10, 145. Academic Press, New York.
Deng, G. and R. Wu. 1983. Methods Enzymol. 100, 96.
Michelson, A.M. and S.H. Orkin. 1982. J. Biol. Chem.257, 14773.
Roychoudhury, R. and R. Wu. 1980. Methods Enzymol.65, 43.
Nelson, T. and D. Brutlag. 1979. Methods Enzymol. 68, 41.
Roychoudhury, R., et al. 1976. Nucleic Acids Res.3, 101.
Bollum, F.J. 1974. In The Enzymes, 3rd edition (ed. P.D. Boyer), Vol. 10, 145. Academic Press, New York.
Legal Information
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
WGK
WGK 2
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service