Specificity
Clone LH7.2 is a mouse monoclonal antibody that detects Collagen VII. It targets an epitope with in the central region of the N-terminal half.
Immunogen
Insoluble fractions of neonatal human foreskin epidermal cells.
Application
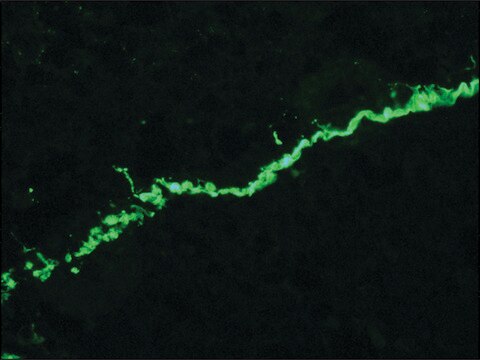
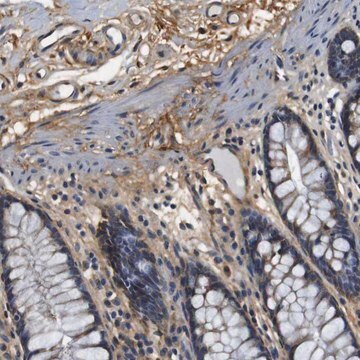
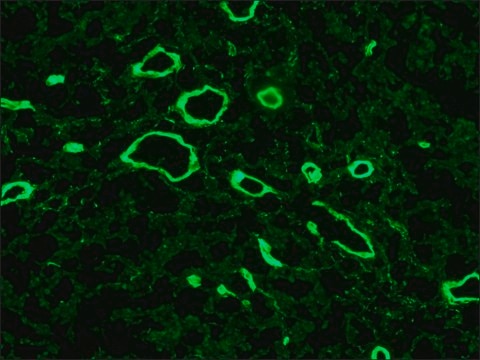
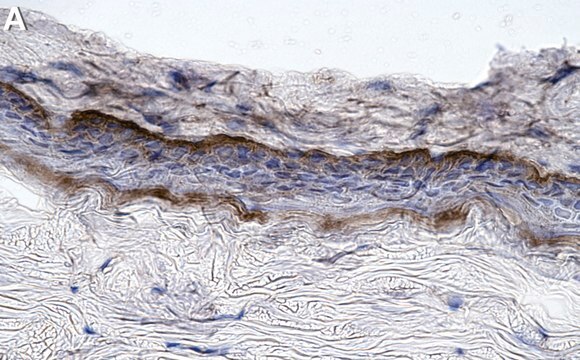
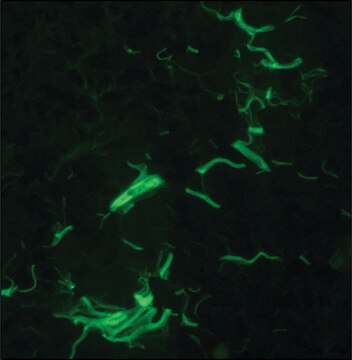
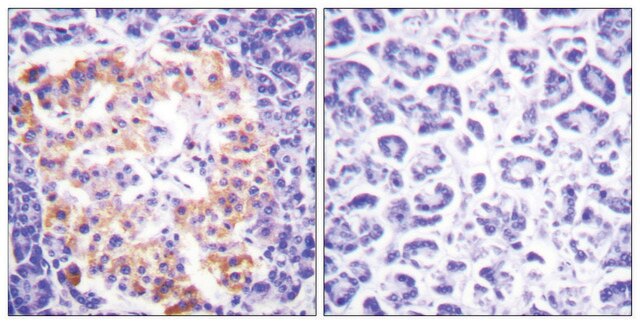
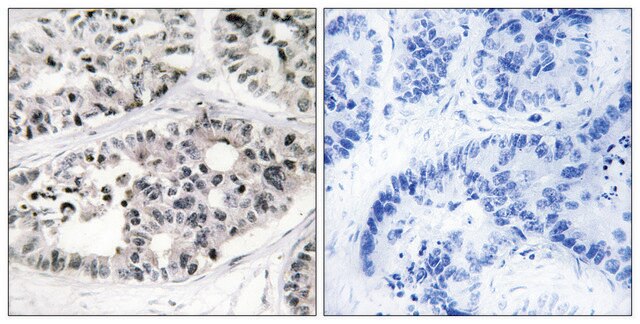
Quality Control TestingEvaluated by Immunocytochemistry in HeLa cell line.Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A 1:25 dilution of this antibody detected Collagen Type VII in HeLa cell line.Tested ApplicationsImmunohistochemistry Applications: A representative lot detected Collagen Type VII in Immunohistochemistry applications (Supp, D.M., et. al. (2019). Cell Transplant. 28(9-10):1242-1256).Immunofluorescence Analysis: A representative lot detected Collagen Type VII in Immunofluorescence applications (Heagerty, A.H., et. al. (1986). J Invest Dermatol. 86(5):603-5).Note: Actual optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user as specimens, and experimental conditions may vary with the end user
Anti-Collagen Type VII, clone LH7.2, Cat. No. MAB1345-I, is a mouse monoclonal antibody that detect Collagen alpha-1(VII) chain and is tested for use in Immunocytochemistry, Immunofluorescence, and Immunohistochemistry.
Target description
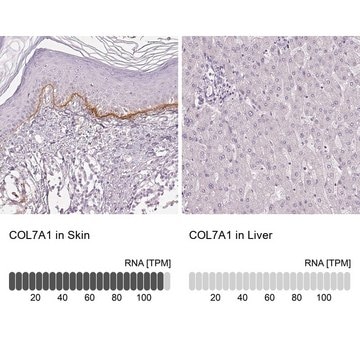
Collagen alpha-1(VII) chain (UniProt: Q02388; also known as Long-chain collagen, LC collagen) is encoded by the COL7A1 gene (Gene ID: 1294) in human. Collagen is the most abundant protein in the body that is predominantly synthesized by fibroblasts. However, epithelial cells may also synthesize small amounts of collagen. The collagen super family includes over 20 different types of collagen with at least 38 distinct polypeptide chains. Collagen type VII is a homotrimeric protein that is primarily synthesized by keratinocytes and skin fibroblasts. It is composed of three identical alpha chains and its distribution is restricted to stratified squamous epithelial basement membrane. It contributes to epithelial basement membrane organization and adherence by interacting with extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins. Type VII collagen contains a non-collagenous domain 1 (NC1), a central collagenous domain, and a non-collagenous domain 2 (NC2) that catalyze the anchoring fibril assembly. Mutations in COL7A1 gene have been linked to epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica, a blistering skin disease characterized by tissue separation that occurs below the dermal-epidermal basement membrane at the level of the anchoring fibrils. Clone LH7.2 is reported to binds to the epidermal basement membrane in normal adult skin and in fetal skin at 10 weeks of gestation. (Ref.: Heagerty, AHM., et al. (1986). J. Invest. Dermatol. 86(5); 603-605; Supp, DM., et al. (2019). Cell Transp. 28(9-10); 1242-1256).
Physical form
Purified mouse monoclonal antibody IgG in buffer containing 0.1 M Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl with 0.05% sodium azide.
Storage and Stability
Stable for 1 year at +2°C to +8°C from date of receipt.
Other Notes
Concentration: Please refer to the Certificate of Analysis for the lot-specific concentration.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.