475870
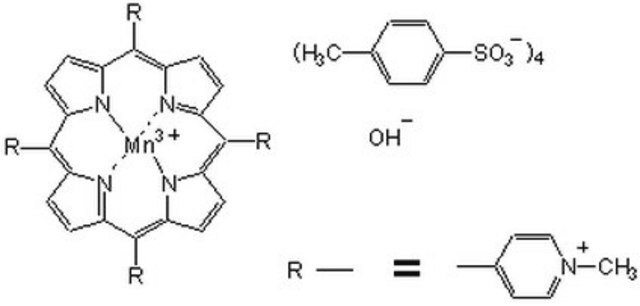
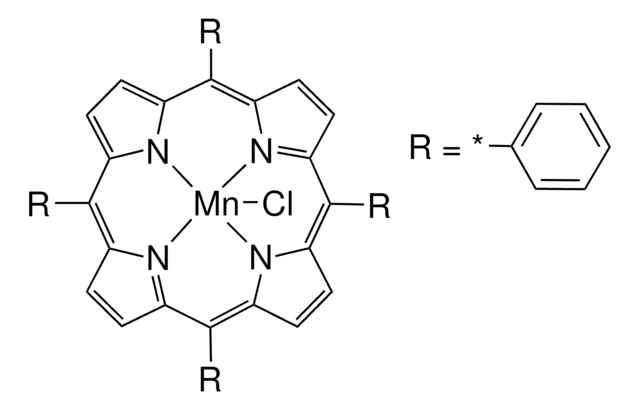
MnTBAP
Cell-permeable superoxide dismutase (SOD) mimetic and peroxynitrite scavenger.
Synonym(s):
MnTBAP, Mn(III)tetrakis(4-benzoic acid)porphyrin Chloride
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C48H28ClMnN4O8
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
879.15
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.77
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥95% (TLC)
form
solid
manufacturer/tradename
Calbiochem®
storage condition
OK to freeze
desiccated
protect from light
color
brown
solubility
aqueous base: soluble
shipped in
ambient
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Cell-permeable superoxide dismutase (SOD) mimetic and peroxynitrite scavenger. Protects endothelial cells in a dose-dependent manner (EC50 ~40 µM) against paraquat (2 mM). Inhibits the oxidation of Dihydrorhodamine 123 (Cat. No. 309825) by peroxynitrite, but does not scavenge nitric oxide (NO).
Cell-permeable superoxide dismutase (SOD) mimetic and peroxynitrite scavenger. Protects endothelial cells in a dose-dependent manner (EC50 ~40 µM) against paraquat (2 mM). Inhibits the oxidation of dihydrorhodamine-123 by peroxynitrite, but does not scavenge nitric oxide (NO).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cell permeable: yes
EC50 ~40 µM in protecting endothelial cells against paraquat (2 mM)
Primary Target
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) mimetic
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) mimetic
Product does not compete with ATP.
Reversible: no
Warning
Toxicity: Standard Handling (A)
Reconstitution
Following reconstitution, aliquot and freeze (-20°C). Stock solutions are stable for up to 6 months at -20°C.
Other Notes
Aladag, M. A., et al. 2003. Acta Neurochir.145, 673.
Szabo, C., et al. 1996. FEBS Lett. 381, 82.
Day, B.J., et al. 1995. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 275, 1227.
Faulkner, K.M., et al. 1994. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 23471.
Szabo, C., et al. 1996. FEBS Lett. 381, 82.
Day, B.J., et al. 1995. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 275, 1227.
Faulkner, K.M., et al. 1994. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 23471.
Legal Information
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
M A Aladag et al.
Acta neurochirurgica, 145(8), 673-677 (2003-10-02)
Delayed cerebral vasoconstriction and brain ischemia, are critical problems in the management of a patient affected by rupture of an intracranial aneurysm. Overexpression of Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase (Cu-Zn SOD) can reduce the extent of cerebral vasospasm. We, therefore investigated if
K M Faulkner et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 269(38), 23471-23476 (1994-09-23)
Several manganic porphyrins, with substituents on the methine bridge carbons, were prepared and examined for stability, redox behavior, catalysis of the dismutation of superoxide radical (O2-), and the ability to protect a superoxide dismutase (SOD)-null strain of E. coli against
C Szabó et al.
FEBS letters, 381(1-2), 82-86 (1996-02-26)
Here we report that the cell-permeable superoxide dismutase mimetic Mn(III)tetrakis (4-benzoic acid) porphyrin (MnTBAP) inhibits the oxidation of dihydrorhodamine-123 by peroxynitrite, but does not scavenge nitric oxide (NO). MnTBAP protects against the suppression of mitochondrial respiration in J774 cells exposed
B J Day et al.
The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics, 275(3), 1227-1232 (1995-12-01)
There is an increased interest in development of therapeutic agents to treat disease states that involve reactive oxygen species in their pathophysiology. The metalloporphyrins, MnTBAP and ZnTBAP, were found to be active in a superoxide dismutase (SOD) assay. The efficacy
Maria Catalina Gomez-Puerto et al.
International journal of molecular sciences, 21(11) (2020-06-14)
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a life-threatening disease characterized by obstructed pulmonary vasculatures. Current therapies for PAH are limited and only alleviate symptoms. Reduced levels of BMPR2 are associated with PAH pathophysiology. Moreover, reactive oxygen species, inflammation and autophagy have
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service