190001P
Avanti
Yeast Extract Polar
Avanti Polar Lipids 190001P, powder
Synonym(s):
Yeast Extract Polar, Yeast Polar Lipid Extract (S. cerevisiae)
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352211
NACRES:
NA.25
Recommended Products
form
powder
packaging
pkg of 1 × 100 mg (190001P-100mg)
manufacturer/tradename
Avanti Polar Lipids 190001P
lipid type
lipid extracts
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Polar Lipid Extract is derived from the total lipid extract by precipitation with acetone followed by extraction of the acetone insoluble material with diethyl ether.
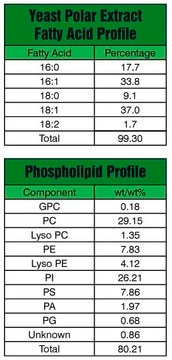
Yeast is rich in sphingolipids. The apolar lipids from yeast separates out first during chloroform/methanol extraction. The aqueous phase contains polar lipids. A total of 162 lipids pertaining to 21 lipid classes are identified in yeast. Phosphatidylinositol comprises the major component of yeast lipid accounting to 17% to 30%.
Biochem/physiol Actions
The total lipids from yeast are useful in understanding lipid metabolism. Yeast lipids serve as model membranes for understanding the lipid raft forming mechanisms. These lipids have a potential to self-organize. The fatty acid composition of polar lipids in yeast are modulated in response to acid stress.
Packaging
5 mL Clear Glass Sealed Ampule (190001P-100mg)
Legal Information
Avanti Research is a trademark of Avanti Polar Lipids, LLC
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Yeast lipids can phase-separate into micrometer-scale membrane domains
Klose C, et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 285(39), 30224-30232 (2010)
Budding Yeast: An ideal backdrop for in vivo lipid biochemistry
Singh P
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 4, 156-156 (2017)
Changes in lipid metabolism convey acid tolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Guo ZP, et al.
Biotechnology for Biofuels, 11(1), 1-15 (2018)
Global analysis of the yeast lipidome by quantitative shotgun mass spectrometry
Ejsing CS, et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 106(7), 2136-2141 (2009)
Joël S Bloch et al.
Nature, 579(7799), 443-447 (2020-02-28)
In eukaryotic protein N-glycosylation, a series of glycosyltransferases catalyse the biosynthesis of a dolichylpyrophosphate-linked oligosaccharide before its transfer onto acceptor proteins1. The final seven steps occur in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and require dolichylphosphate-activated mannose and glucose
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service