RAB0422
Human E-Selectin ELISA Kit
for serum, plasma, cell culture supernatants and urine
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Speziesreaktivität
human
Verpackung
kit of 96 wells (12 strips x 8 wells)
Methode(n)
ELISA: suitable
capture ELISA: suitable
Aufnahme
sample type urine
sample type plasma
sample type cell culture supernatant(s)
sample type serum
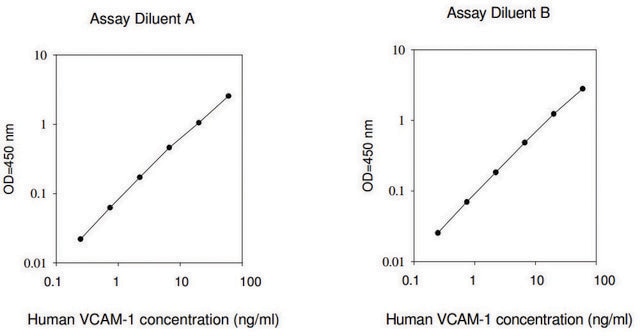
assay range
inter-assay cv: <12%
intra-assay cv: <10%
sensitivity: 30 pg/mL
standard curve range: 24.69-18000 pg/mL
Nachweisverfahren
colorimetric
Versandbedingung
wet ice
Lagertemp.
−20°C
Angaben zum Gen
human ... SELE(6401)
Verwandte Kategorien
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Immunogen
Anwendung
Please refer to the attached General ELISA KIT Procedure (sandwich, competitive & Indirect ELISA)
Sonstige Hinweise
Please type the word sample in the text box provided for lot number.
Kit-Komponenten auch einzeln erhältlich
Signalwort
Warning
H-Sätze
P-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Met. Corr. 1
WGK
WGK 3
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.