F0518
Ferrous sulfate chelate solution
100 ×, suitable for plant cell culture
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC-Code:
10171502
NACRES:
NA.72
Empfohlene Produkte
Sterilität
sterile-filtered
Qualitätsniveau
Form
solution
Konzentration
100 ×
Methode(n)
cell culture | plant: suitable
Anwendung(en)
agriculture
Lagertemp.
2-8°C
Verwandte Kategorien
Anwendung
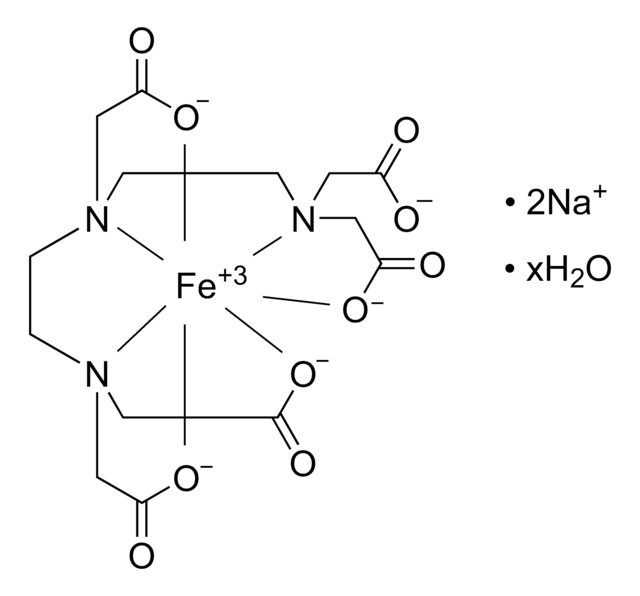
Ferrous:EDTA chelate is a redox active form of bound iron. Ferrous:EDTA chelate will give up its iron to plant iron chelators. This iron chelate may be useful in a wide range of studies on iron metabolism and regulation in plants and plant oxidative processes.
Komponenten
Contains 2.785 g/L FeSO4 ⋅ 7H2O and 3.725g/L EDTA 2Na ⋅ 2H2O
WGK
WGK 1
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Abhishek Jain et al.
Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 102(10), 4563-4575 (2018-04-05)
Nickel (Ni(II)) toxicity is addressed by many different bacteria, but bacterial responses to nickel stress are still unclear. Therefore, we studied the effect of Ni(II) toxicity on cell proliferation of α-proteobacterium Caulobacter crescentus. Next, we showed the mechanism that allows
T Franza et al.
Molecular plant-microbe interactions : MPMI, 12(2), 119-128 (1999-02-02)
Low iron availability is a triggering signal for coordinated expression of the genes encoding pectate lyases PelB, PelC, PelD, and PelE, and chrysobactin iron transport functions, which are two main determinants of phytopathogenicity of the Erwinia chrysanthemi strain 3937. The
Neeraja Vajrala et al.
BMC microbiology, 11, 37-37 (2011-02-23)
In response to environmental iron concentrations, many bacteria coordinately regulate transcription of genes involved in iron acquisition via the ferric uptake regulation (Fur) system. The genome of Nitrosomonas europaea, an ammonia-oxidizing bacterium, carries three genes (NE0616, NE0730 and NE1722) encoding
Jaita Pal et al.
Indian journal of experimental biology, 48(12), 1210-1218 (2011-01-22)
Cellular damage caused by reactive oxygen species has been implicated in several diseases and hence antioxidants have significant importance in human health. Cold water, hot water and methanolic extract of Pleurotus squarrosulus were evaluated for antioxidant activity against hydroxyl radical
Luis A Sayavedra-Soto et al.
Methods in enzymology, 486, 403-428 (2010-12-28)
The chemolithoautotroph Nitrosomonas europaea oxidizes about 25 mol of NH(3) for each mole of CO(2) that is converted to biomass using an array of heme and nonheme Fe-containing proteins. Hence mechanisms of efficient iron (Fe) uptake and homeostasis are particularly
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.