901034
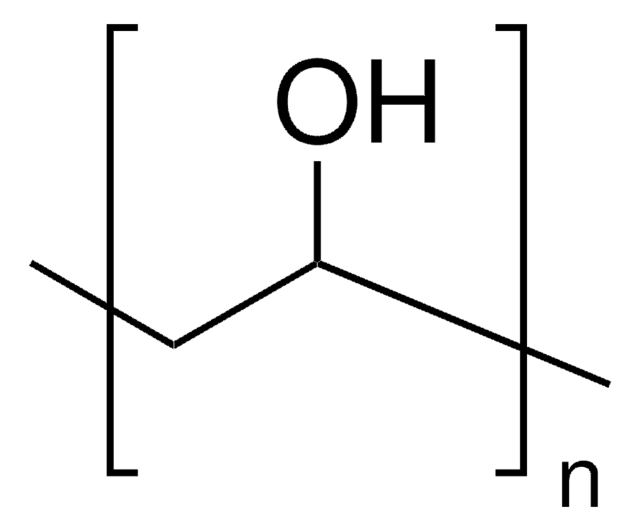
Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) blend printing filament
1.75 mm
Synonym(e):
AtlasSupport™, PVA blend filament
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualitätsniveau
Beschreibung
Filament roundness: ≥95%
Melt flow rate: 2.3 g/10 min
Melt temperature: ±163 °C
Print temperature: ±180-205 °C
Specific gravity: 1.22 g/cc
Spool Hub Diameter: 52 mm
Spool Size (DxH): 200 mmx55 mm
Vicat softening temperature: ± 60.2 °C
Form
solid (filament)
Farbe
orange, natural
Durchmesser
1.75 mm±0.05 mm (filament diameter)
InChI
1S/C2H4O/c1-2-3/h2-3H,1H2
InChIKey
IMROMDMJAWUWLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Verwandte Kategorien
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
Rechtliche Hinweise
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flammpunkt (°F)
49.5 °F - closed cup
Flammpunkt (°C)
9.7 °C - closed cup
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.