447951
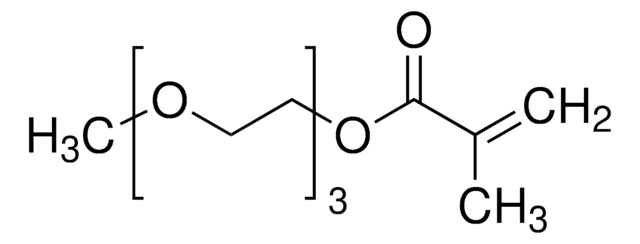
Poly(ethylenglycol)methylethermethacrylat
average Mn 950, contains 100 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor, 300 ppm BHT as inhibitor
Synonym(e):
Methoxy-PEG-methacrylat, Methoxy-poly-(ethylenglykol)-monomethacrylat, Poly-(ethylenglykol)-monomethylether-monomethacrylat
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Form
solid
Qualitätsniveau
Mol-Gew.
average Mn 950
Enthält
100 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor
300 ppm BHT as inhibitor
Eignung der Reaktion
reagent type: chemical modification reagent
reaction type: Polymerization Reactions
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
33-38 °C
Dichte
1.1 g/mL at 25 °C
Ω-Ende
methacrylate
α-Ende
methoxy
Polymerarchitektur
shape: linear
functionality: monofunctional
Lagertemp.
2-8°C
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Verwandte Kategorien
Anwendung
- Redox-Responsive "Catch and Release" Cryogels: A Versatile Platform for Capture and Release of Proteins and Cells.: This study introduces innovative cryogels incorporating Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate, emphasizing their applications in protein and cell capture and release systems. These cryogels exhibit redox-responsive behavior, making them suitable for advanced biomedical applications, including targeted drug delivery and tissue engineering (Calik et al., 2024).
- Study of mechanical property and biocompatibility of graphene oxide/MEO(2)MA hydrogel scaffold for wound healing application.: The research explores the mechanical properties and biocompatibility of a hydrogel scaffold combining graphene oxide and Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate (PEGMEM). This scaffold shows potential for enhanced wound healing applications due to its robust mechanical strength and excellent biocompatibility (Luong et al., 2024).
- Constructing the Polymer Molecules to Regulate the Electrode/Electrolyte Interface to Enhance Lithium-Metal Battery Performance.: This paper highlights the role of Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate in developing polymer molecules that regulate electrode/electrolyte interfaces. The findings demonstrate significant improvements in lithium-metal battery performance, pointing to the material′s potential in energy storage applications (Chen et al., 2024).
- Helical Superstructures from the Hierarchical Self-Assembly of Coil-Coil Block Copolymer Guided by Side Chain Amyloid-β(17-19) LVF Peptide.: This study explores the self-assembly of block copolymers incorporating Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate, leading to the formation of helical superstructures. The work suggests applications in nanotechnology and materials science, particularly for creating novel biomaterials (Nayak et al., 2024).
- Minimalist Nanovaccine with Optimized Amphiphilic Copolymers for Cancer Immunotherapy.: This research presents a minimalist nanovaccine utilizing optimized amphiphilic copolymers, including Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate. The nanovaccine shows promise in enhancing cancer immunotherapy by improving the immune response and targeting efficiency (Niu et al., 2024).
Signalwort
Warning
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT SE 3
Zielorgane
Respiratory system
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flammpunkt (°F)
230.0 °F - closed cup
Flammpunkt (°C)
> 110 °C - closed cup
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
Progress in biotechnology fields such as tissue engineering and drug delivery is accompanied by an increasing demand for diverse functional biomaterials. One class of biomaterials that has been the subject of intense research interest is hydrogels, because they closely mimic the natural environment of cells, both chemically and physically and therefore can be used as support to grow cells. This article specifically discusses poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels, which are good for biological applications because they do not generally elicit an immune response. PEGs offer a readily available, easy to modify polymer for widespread use in hydrogel fabrication, including 2D and 3D scaffold for tissue culture. The degradable linkages also enable a variety of applications for release of therapeutic agents.
Devising biomaterial scaffolds that are capable of recapitulating critical aspects of the complex extracellular nature of living tissues in a threedimensional (3D) fashion is a challenging requirement in the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.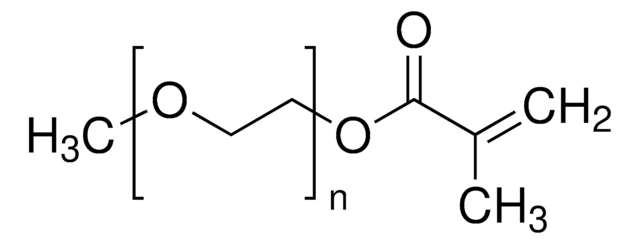

![PSS-[3-(2-Aminoethyl)amino]propyl-Heptaisobutyl, substituiert](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/583/905/1ee2f0b3-2da3-49d4-af68-a0382b34aeff/640/1ee2f0b3-2da3-49d4-af68-a0382b34aeff.png)